Ask the AI Tutor
Need help with Crude Oil 2? Ask our AI Tutor!
AI Tutor - Lucy
Connecting with Tutor...
Please wait while we establish connection

An oil platform at sea drilling for crude oil. Learn more about crude oil with this quiz.
Crude Oil 2
Crude oil contains many hydrocarbons that behave differently. This GCSE Chemistry quiz checks how we classify them, predict properties, and link structure to fuel use.
1 .
The diagram shows the apparatus used in the laboratory for the distillation of liquids. Pick the correct label for B.
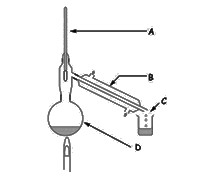
Distillate
Condenser
Round bottom flask
Thermometer
This is sometimes called a Leibig condenser
2 .
Pick the correct label for C.

Distillate
Condenser
Round bottom flask
Thermometer
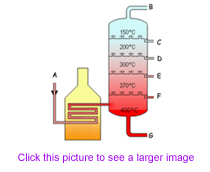
When distilling crude oil, the properties of the distillate depend on the temperature at which it boils
3 .
4 .
5 .
6 .
7 .
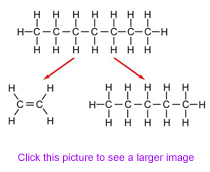
The diagram shows the process of cracking a long chain hydrocarbon into two smaller hydrocarbons. Pick the correct name of the starting alkane.
Pentane
Heptane
Ethane
Decane
If you count the carbon atoms, you see that the starting alkane has seven in its chain. 7 = hept just like a 7-sided shape is a heptagon
8 .
9 .
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions.
Ready for more?
Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's
not all...
not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions. Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉