Ask the AI Tutor
Need help with Manufacturing Processes? Ask our AI Tutor!
AI Tutor - Lucy
Connecting with Tutor...
Please wait while we establish connection

Ordinary items, such as tinsel, need people to have some knowledge of how chemical reactions take place. (Photo courtesy of jiva at Flickr.)
Manufacturing Processes
Big chemical industries rely on smart choices about conditions and cost. This GCSE Chemistry quiz explores manufacturing processes, including yields, rates, equilibrium, and why industry uses compromises.
Click on any picture to see a larger image
1 .
2 .
3 .
4 .
The diagram shows a field of yellow flowers. The yellow flowers are of the rapeseed plant. The oil from the seeds of this plant are used as vegetable oil. Sometimes this oil is hardened to make a spread. What process is undertaken to change the liquid oil into a solid spread?
Thermal decomposition
Polymerisation
Hydrogenation
Esterification
Hydrogen is added to the oil at about 60°C in the presence of a nickel catalyst
5 .
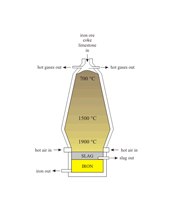
The picture is a photograph of a limestone quarry near Ancaster in Lincolnshire. What process does limestone have to be subjected to in order to be changed into calcium oxide (quicklime)?
Thermal decomposition
Polymerisation
Hydrogenation
Esterification
The equation for the thermal decomposition of limestone is CaCO3 ? CaO + CO2
6 .
7 .
The scent of many fruits is due to a group of chemicals called esters. By what process are esters produced?
Thermal decomposition
Polymerisation
Hydrogenation
Esterification
Esterification is the process of reacting an alcohol with a carboxylic acid to produce an ester in the presence of sulfuric acid (acting as a catalyst)
8 .
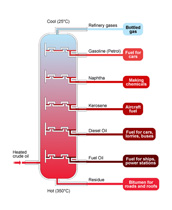
The photograph is of distillation apparatus. What physical property does distillation use to separate liquids?
Melting point
Viscosity
Boiling point
Volatility
When a mixture is heated, the temperature 'sticks' as one of the liquids boils. When it has completely boiled off, the temperature will start to rise again until the next component boils
9 .
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions.
Ready for more?
Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's
not all...
not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions. Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉