Ask the AI Tutor
Need help with The Earth and its Atmosphere 2? Ask our AI Tutor!
AI Tutor - Lucy
Connecting with Tutor...
Please wait while we establish connection
Earth - the beautiful planet we call home.
The Earth and its Atmosphere 2
Revise GCSE Chemistry atmosphere change: learn how oxygen built up, how carbon dioxide reduced, and what evidence supports these ideas over time. Read the notes, then try the quiz below.
Click on any picture to see a larger image
1 .
2 .
3 .
4 .
5 .
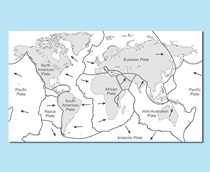
The photograph is of Mount St. Helens in the US. The volcano erupted in 1980, killing 57 people. Where are volcanoes most likely to be formed?
When two continental plates meet
When a continental and an oceanic plate meet
When two plates move in different directions next to each other
When two plates move away from each other
When a continental and an oceanic plate meet, the less dense continental plate slides over the top of the oceanic plate and this is called subduction. The oceanic plate is remelted and the magma rises and forms a volcano
6 .
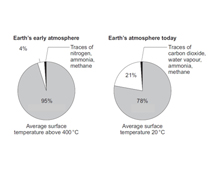
The diagram shows the percentage of different gases in the atmosphere today and the Earth's early atmosphere. Pick the correct value for the gas with 95% abundance in the early atmosphere.
(Click on the picture to enlarge it.)
(Click on the picture to enlarge it.)
Carbon dioxide
Nitrogen
Oxygen
Water vapour
The gases of the atmosphere are believed to have come from volcanic eruptions
7 .
8 .
The picture is of the aftermath of an earthquake that hit Kobe in Japan in 1995. What causes earthquakes to happen in Japan?
Two continental plates meeting
A continental and an oceanic plate meeting
Two plates moving in different directions next to each other
Two plates moving away from each other
This movement creates friction so the plates don't move smoothly, creating earthquakes
9 .
The photograph is of Earth from space. There are layers of gases between the Earth and space. The effect of which layer being damaged can increase the incidence of skin cancers amongst people on Earth?
Layer of hydrogen and helium
Layer of CO2
Ozone layer
Mesosphere
The ozone layer protects us from the harmful effects of UV rays from the Sun
10 .
The picture shows the aftermath of the earthquake and tsunami that hit Japan in March of 2011. Why is it difficult to predict when earthquakes will occur?
We don't know what causes earthquakes
Earthquakes have no known cause and are completely random
We can predict where an earthquake will happen
Interactions between tectonic plates are very complex
The movement of tectonic plates is not smooth, sometimes the rocks lock together. The plates continue to move and so the rocks are put under strain. There are so many factors involved, it is currently impossible to know when the rocks will become 'unstuck'. When they do, this causes an earthquake
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions.
Ready for more?
Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's
not all...
not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions. Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉