
Ask the AI Tutor
Need help with Electricity - Transformers? Ask our AI Tutor!
AI Tutor - Lucy
Connecting with Tutor...
Please wait while we establish connection
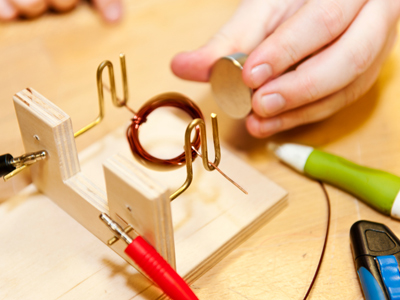
A magnet can be used to induce a potential difference at the ends of a coil of wire.
Electricity - Transformers
Transformers change the voltage in a circuit so electricity can be transmitted efficiently and used safely. This quiz checks your understanding of step-up and step-down transformers.
1 .
What is induced across the ends of an electrical conductor which moves through a magnetic field?
A potential difference
A resistance
A current
A capacitance
Potential difference is often referred to as voltage
2 .
What can be used to induce a potential difference at the ends of a coil of wire?
Heat
A vacuum
Magnet
Bread
Moving a magnet inside the coil produces a changing magnetic field, causing a potential difference to build. A potential difference is only induced for as long as the magnet is moving
3 .
Considering the basic structure of a transformer, what does an alternating current in a primary coil produce in the iron core which it surrounds?
A static magnetic field
A changing magnetic field
A static electric field
A changing electric field
The iron core concentrates the magnetic field and ensures that it passes directly through the secondary coil
4 .
In a step-up transformer, is the potential difference created in the secondary coil more, less or equal to the potential difference in the primary coil?
More
Less
Equal
Values for the coils are required to calculate this
Knowing that the transformer is a step-up transformer is enough to know that the potential difference will be greater in the secondary coil than the first
5 .
In a step-down transformer, is the potential difference created in the secondary coil more, less or equal to the potential difference in the primary coil?
More
Less
Equal
Values for the coils are required to calculate this
Step-down (and step-up) refers to voltage, remembering that small fact will help you in transformer and perhaps National Grid exam questions
6 .
Which equation correctly relates the potential difference across the primary and secondary coils of a transformer?
Vp⁄Vs = np⁄ns
Vp⁄Vs = ns⁄np
Vs⁄Vp = np⁄ns
Vp⁄Vp = np⁄ns
If a transformer was assumed to be 100% efficient, the electrical power output would equal the electrical power input. Thus the following formula would also be true: Vp x Ip = Vs x Is
7 .
Which types of transformers operate at high frequency?
Laminated core
Variac
Stray field
Switch mode transformers
These are useful in phone, tablet and laptop chargers
8 .
What is an advantage of using switch mode transformers over a traditional transformer when working from a 50 Hz mains supply?
They change the electricity at a quicker rate
They are lighter and smaller
They are more robust
They are more efficient
They are therefore more portable and can easily slip into your luggage when going on a school trip or holiday
9 .
What is another advantage of using switch mode transformers when no load is applied?
They use little power
They use lots of power
They store electricity
There is no advantage offered by switch mode transformers when no load is applied
One of the issues with normal transformers is that when an appliance is switched on but in standby mode, the transformer is still operating at almost full power, which is a waste of energy
10 .
A primary coil within a transformer has 48 turns around its coil and has a potential difference applied to it of 12 V. If the secondary coil has 60 turns around its coil, what is the potential difference produced at the ends of the secondary coil?
12 V
14 V
15 V
9.6 V
Either use the transformer equation or simple proportion to arrive at the correct answer. Because the secondary coil is larger than the primary, you should already know the potential difference should be greater which immediately eliminates two of the answers
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions.
Ready for more?
Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's
not all...
not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions. Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉






