Unit 2 - Cell Structure
Students of GCSE Biology will be expected to familiarise themselves with the various features of plant and animal cells, such as the nucleus or the mitochondria for example. This quiz on cell structure will help them to do just that.
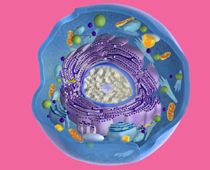
In the early 1800s, Scottish scientist Robert Brown was examining plant cells under a microscope when he noticed that there was a similar structure in each and every cell he looked at. It had been seen before but it was Brown who first realised it was present in all plant cells, and he called it ‘the nucleus’.
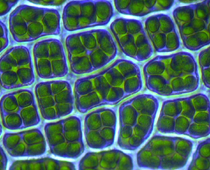
We now know that animal and plant cells have many features in common - a nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes and a cell membrane. Plant cells have chloroplasts for photosynthesis, a permanent vacuole and a cell wall. Brown had no idea of the importance of the nucleus, or that it was also found in animal cells too, but scientists have gradually discovered more and more about how cells work.
Ready for more?
not all...
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.