
Ask the AI Tutor
Need help with Hurricanes? Ask our AI Tutor!
AI Tutor - Lucy
Connecting with Tutor...
Please wait while we establish connection
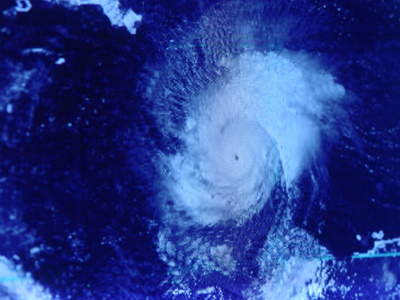
See if you can get full marks in this enjoyable quiz.
Hurricanes
Hurricanes are powerful tropical storms with strong winds and heavy rain. This GCSE Geography quiz tests how and where they form, move and cause damage.
1 .
Which of the following is not a reason why there is a larger loss of life in LEDCs than MEDCs during a hurricane?
The storm warning systems are better in MEDCs
MEDCs can afford to plant trees to shelter urban centres from storms
Richer countries can afford to build more hurricane shelters
MEDCs can begin disaster relief operations much sooner than LEDCs
There are other reasons too such as higher literacy rates so populations understand the dangers and what they should do to stay safer during a hurricane, better hurricane survival education programmes and more sturdily-constructed buildings
2 .
Why does a hurricane lose strength when it is over a land mass?
The trees and buildings absorb the energy
The sun shines more over the sea than land
It gets its energy from warm moist air rising from the sea
Over land, the eye changes shape
There is not as much warm moist air over land as there is at sea so there is a lot less energy to power the hurricane
3 .
The centre of a hurricane is called the ...
ear
nose
eye
throat
It is an area that is clear of clouds because it is where cold air is sinking downwards. Clouds only form from rising warm air that cools down at higher altitudes
4 .
In 2005, hurricane Katrina devastated New Orleans in the south of the USA. Much of the city was flooded but what was the main cause of the flooding?
Heavy rain
Rivers bursting their banks because of the rain
Blocked drains
A storm surge
The strong winds of a hurricane create a bulge of water which is called a storm surge. In the case of New Orleans, the surge was about 6m. The flood defences were poorly constructed and failed to stop the surge from entering the city
5 .
Where do hurricanes form?
At the equator
Between 5 and 10 degrees north of the equator
Between 5 and 20 degrees from the equator
More than 45 degrees from the equator
Further away from the equator, the seas never become warm enough to start a hurricane. The rising air must be rotating, any closer to the equator than 5 degrees and the coriolis force is too weak to cause rotation
6 .
Which of the following is not a hazard to human settlements caused by hurricanes?
Earthquakes
Flooding
Destruction of buildings
Damage to communications networks
There is no link between earthquakes and hurricanes
7 .
To be called a hurricane, the wind speed in a storm must be ...
between 0 and 20 mph
between 20 and 37 mph
between 35 and 55 mph
at least 75 mph
If you are caught outside in a hurricane, it would be difficult to walk, lighter people may not even be able to stand upright. The biggest problem would be avoiding being hit by flying debris - imagine even just a small object hitting you at a similar speed to a car driving along a motorway in the fast lane ...
8 .
What temperature must the sea be for a hurricane to form?
Less than 25°C
At least 26°C
Between 0 and 10°C
50°C
Where the sea surface temperature is 26°C or more, it is possible for a hurricane to form. Once a hurricane forms, it can travel long distances
9 .
Which of the following is not a name for a tropical revolving storm?
Tornado
Typhoon
Hurricane
Cyclone
A tornado is much smaller and is also called a whirlwind
10 .
Where do hurricanes usually form?
In a tropical rainforest
In the northern hemisphere
Over polar seas
Over tropical seas
Hurricanes require rising air that contains a lot of moisture, warm air rises and can hold more moisture than cold air. Warm air over a warm sea can hold the greatest amount of moisture
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions.
Ready for more?
Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's
not all...
not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions. Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉






