Ask the AI Tutor
Need help with OS Maps: Landscape Features? Ask our AI Tutor!
AI Tutor - Lucy
Connecting with Tutor...
Please wait while we establish connection

How many landscape features do you recognise?
OS Maps: Landscape Features
Ordnance Survey maps show both natural and human landscape features. Learn how to recognise quarries, reservoirs, valleys, and slopes so you can visualise places from symbols alone.
To see a larger image, click on the picture.
1 .
2 .
3 .
4 .
5 .
6 .
Which of the following statements is correct?
This diagram represents a frost shattered peak in a mountain range
This diagram represents an area where stone has been quarried
This diagram represents the lower course of a river
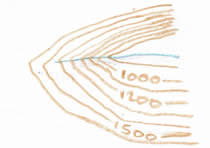
This diagram represents part of the upper course of a river
The clues are that the contour lines show very high ground, contour lines close together, the sharp V-shape of the contour lines and the thin blue line with no meanders showing the stream
7 .
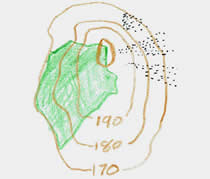
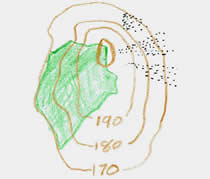
This sketch map was prepared for a 1:50,000 scale OS map. The green area on it shows:
a mixed woodland
a broadleafed woodland
an orchard
a field
Broadleafed woodland would have small broadleaf trees drawn on it, a conifer woodland would have small pine trees drawn on it. An area of plain green on an OS 1:50,000 map indicates a mixed woodland with both conifers and broadleafed trees
8 .
9 .
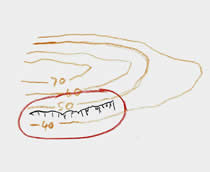
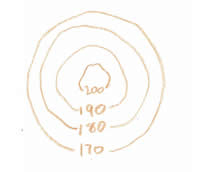
This sketch map was made by a geographer carrying out their fieldwork. What landscape feature would be seen in the area indicated by the red ring on the sketch?
Railway
Rocky outcrops
A vertical cliff
Moorland
The small black curves are used to indicate and area where there are a lot of surface rocks visible
10 .
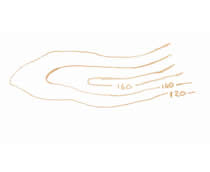
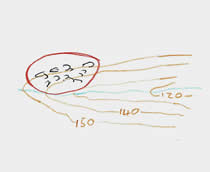
A student preparing for fieldwork made several sketches of landscape features they expected to see. This sketch represents:
a fast-flowing mountain stream
the confluence of two rivers
a wave-cut platform
a road junction
Wide blue lines on OS maps represent rivers and where two rivers join is called a confluence
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions.
Ready for more?
Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's
not all...
not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions. Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉