Biology - Microorganisms and Disease (AQA)
One of the topics covered in GCSE Science is the requirements for keeping healthy. This is the third of six quizzes looking at this subject and it concentrates in particular on microorganisms, such as bacteria or fungi, which cause disease.
It's hard to believe but there was a time when doctors who performed operations, examinations and post mortems did not wash their hands at all. The reason was that there was no 'germ theory'. They had no idea of the existence of microorganisms and no idea that some of these were pathogenic (create infectious diseases). Microorganisms are microscopic, living, single-celled organisms such as bacteria. Sometimes people refer to viruses as microorganisms, which they are not. Viruses are not alive, they are simply a strand of DNA in a protein coating.
The first steps towards the levels of hygiene that we know and use today came in the middle of the 19th Century when a Hungarian doctor, Ignaz Semmelweis, realised that disease was transferred from one patient to another on the hands of doctors. So he instructed his team to wash their hands in between working on different patients. The result was spectacular and immediate - patient deaths dropped dramatically.
There was no understanding of how this worked as the bacteria which cause infections had not been discovered. Because of this his idea was not accepted by other doctors at the time, even though the results were obvious. About 20 years after Semmelweis's discovery, French scientist Louis Pasteur came up with the 'germ theory'. He showed that food went off because of contamination by microorganisms from the air and argued that these could cause disease. His theory backed up what Semmelwies had said many years before and led to the development of antiseptics.
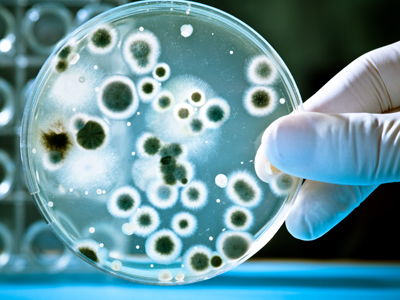
Careful studies of pathogenic microorganisms can be carried out in a laboratory to find the most effective ways of defending against them. This is done using petri dishes partially filled with a nutrient gel. All of the equipment used has to be extremely well sterilised beforehand in order that the results are accurate. Growing microorganisms in a school laboratory could be dangerous so to keep the risks low, the cultures (sealed petri dish plus contents) are kept at temperatures of no higher than 25oC.
Ready for more?
not all...
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.







