
Ask the AI Tutor
Need help with Unit 2 - Stem Cells? Ask our AI Tutor!
AI Tutor - Lucy
Connecting with Tutor...
Please wait while we establish connection
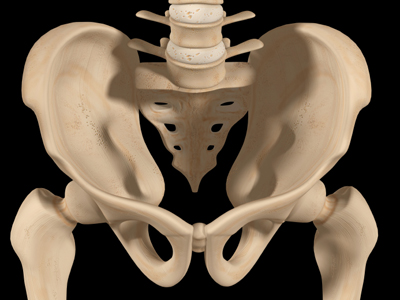
Doctors take bone marrow from the donor's hip bone.
Unit 2 - Stem Cells
Test your GCSE Biology knowledge of stem cells, how they specialise, and why scientists hope to use them to repair damaged tissues in the future.
1 .
A human stem cell can develop into what?
Some cells
Only nerve cells
Only ears
Any type of human cell
Once they have developed into a specialised cell, they will remain in that form
2 .
Stem cells in adults can be found mainly in which location?
Blood
Heart
Bone marrow
Brain
Stem cells can be extracted from adult bone marrow
3 .
Can stem cells can be grown in a lab?
No
Yes
Sometimes
Never
Stem cells can be grown in a special dish in a lab and can then be used in operations to replace parts of the body
4 .
Stem cells can be removed from which stage of human development?
Egg
Sperm
Zygote
Embryo
Umbilical cord blood contains stem cells and can be used to treat some blood disorders in the brothers or sisters
5 .
Some people object to stem cell research saying it is...
expensive
unethical
a waste of resources
against God
The ethical debate continues over the use of human embryos in research
6 .
When a cell develops into its specialised cell type, what is it called?
Undifferentiated
Redifferentiated
Differentiated
Dedifferentiated
Stem cells become differentiated cells
7 .
Stem cells could be used to cure paralysis. Which type of cell would they need to become?
Heart
Liver
Kidney
Nerve
Paralysis is usually caused by broken nerves or nerve disorders
8 .
We can cure certain types of leukaemia using cells from which part of the body?
The blood
The muscles
The bone marrow
The heart
Leukaemia is a form of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. Adult bone marrow contains stem cells that could be used in leukaemia treatment
9 .
Bone marrow can be provided by donors. Where do doctors take the bone marrow from?
Hip bone
Thigh bone
Arm bone
Neck vein
Donors can also receive injections to stimulate stem cells to appear in the blood which is removed through a vein. This is a newer procedure
10 .
To avoid ethical issues concerning embryos in the future, stem cells may be taken from which source?
Mice
Prisoners
Umbilical cords
Blood
After birth, the human umbilical cord is expelled from the womb and then discarded
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions.
Ready for more?
Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's
not all...
not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉
**Unlimited Quizzes Await You! 🚀**
Hey there, quiz champ! 🌟 You've already tackled today's free questions. Ready for more?
🔓 Unlock UNLIMITED Quizzes and challenge yourself every day. But that's not all...
🔥 As a Subscriber you can join our thrilling "Daily Streak" against other quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.
Don't miss out! Join us now and keep the fun rolling. 🎉






